成都环城生态公园生态景观规划
The Landscape Plan of the Eco-Park Belt in Chengdu
-
项目地点:四川成都
项目业主:成都市风景园林规划设计院
面积:18615 ha
设计时间:2020年
获奖:2022国际风景园林师联合会亚非中东地区(IFLA AAPEM)分析与规划类荣誉奖
-
Project location:Chengdu, Sichuan Province
Clients:Chengdu Landscape and Garden Planning and Design Institute
Area:18615 ha
Design year:2020
Award:2022 IFLA AAPEM Award in Analysis and Master Planning(Honourable Mention)
背景与任务
Background and Objectives
成都是一座位于青藏高原东缘、雪山脚下的特大城市。2000多年前建成的都江堰水利工程将岷江水引入成都平原,形成“梳状水系”支撑下富庶的灌溉农业区和与自然充分融合的城镇人居体系,千百年来被称为“天府之国”,是中国传统人居智慧的典范。2018年以来,成都开始建设中国第一个“公园城市”示范区,期望在城镇化水平快速提升的背景下,延续传统人居生态智慧,遏制和修复城市扩张发展对生态景观格局的侵占和破坏,提升区域绿色空间营造质量,重新连接高密度城市的人们回归自然环境。
Chengdu is a unique mega city located at the foot of snow mountains of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. The Dujiangyan Weir, built more than 2,000 years ago, forms a "comb-shaped irrigation system" to support prosperous agrarian areas around this city. Since 2018, Chengdu has become China' s first pilot “Park City". It expects that in there of rapid urbanization, the traditional ecological wisdom of human settlements within nature can be inherited, and damages of the landscape pattern caused by urban sprawl can be restored. Also, it expects to improve the quality of regional green spaces, and to reconnect people in high-density cities to the natural environment.
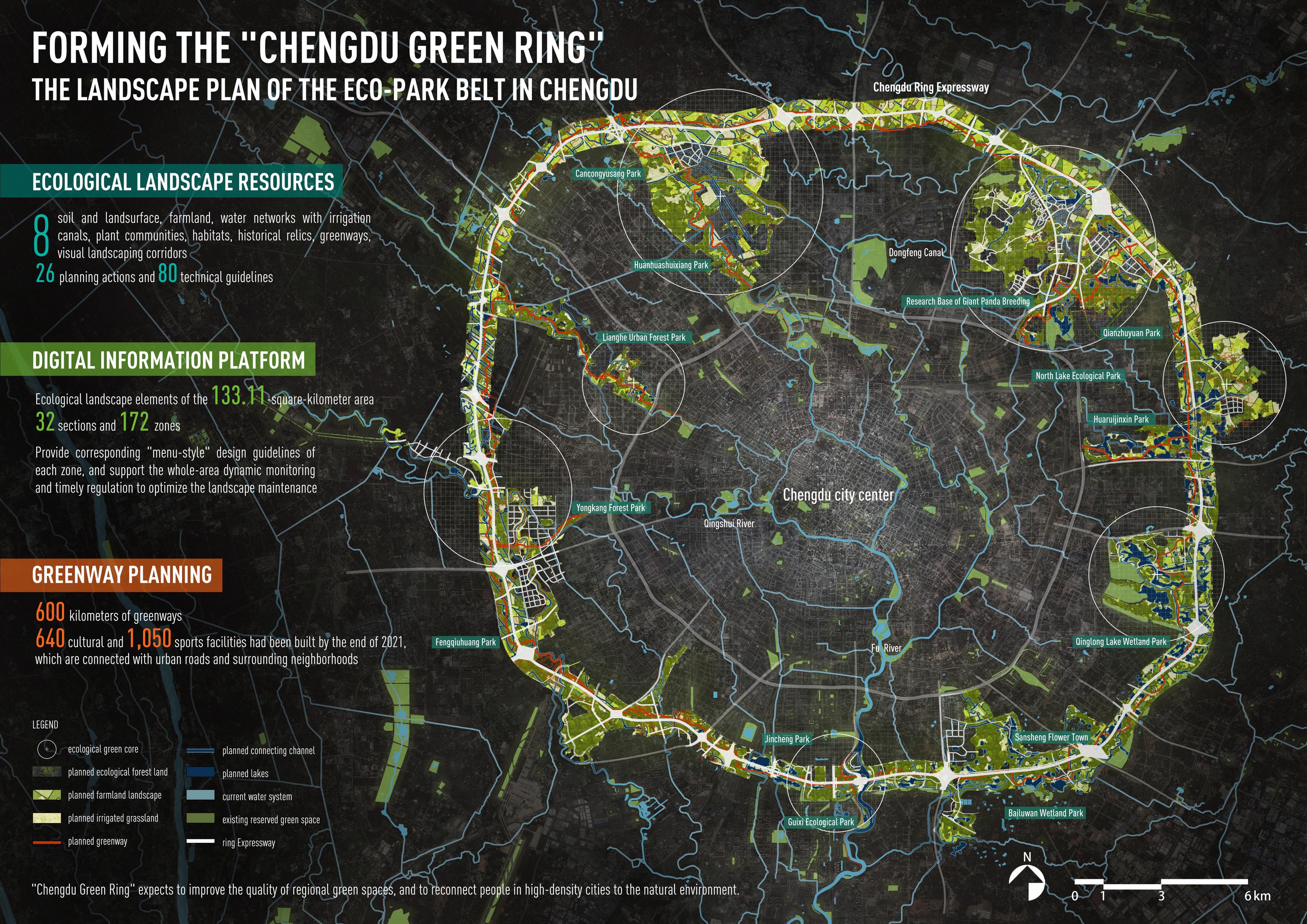
成都环城生态公园是公园城市建设的核心项目,位于城市中心区外围,总面积133.11平方公里。规划旨在整合、利用现有城市内外各建设片区之间分散的开放空间,形成“环状+楔形”区域尺度绿色空间的纽带,塑造连贯、有韧性的、有吸引力和承载多元场景的公园系统。
Chengdu Eco-Park Belt is the flagship project for the "Park City". It locates in the periphery of the city center with a total area of 133.11 km2. This project aims to integrate the fragmented "residual" open spaces between the existing construction areas inside and outside the city (including road green belts, river corridors, wetlands, farmland, hills, country parks, and brown field after the demolition of industrial plants, etc.), and form a successive "ring+ wedge" regional green belt, and create a coherent, resilient, attractive, and multi-scenario park system.
现实与挑战
Realities and Challenges
本项目面临的核心挑战在于:如何采取有效的系统性策略,有效的扭转对千百年来形成的成都平原灌区良好原生生态景观格局的破碎化和退化趋势,并重塑一个生态安全、有韧性、有吸引力、可进入、可持续更新的“成都绿环”?
Overall, the core challenge facing this project is: how to adopt systematic strategies to conserve the good original landscape pattern of Chengdu Plain Irrigation Area formed over thousands of years, effectively reverse its fragmentation and degradation trends, and reshape a natural-driven, resilient, accessible, and attractive "Chengdu Green Ring"?
具体而言,在既往城市建成区的快速扩张期,成都环城生态公园范围内的用地大多被作为城乡之间的“剩余空间”,传统农耕与人居体系已经解体,对城市近郊绿色空间的生态价值缺乏充足认知,而包含诸多生态景观要素的规划引领体系尚未建立。现阶段的主要问题表现如下:
Specifically, after the rapid urban sprawl in past decades, the traditional farming and human settlement system in most areas within Chengdu Eco-Park Belt has tended to disintegrate. There were lacks neither sufficient understanding of ecological value of these peripheral green spaces, nor effective long-term consideration of the use of the land. To be detailed, there are current problems as follows:
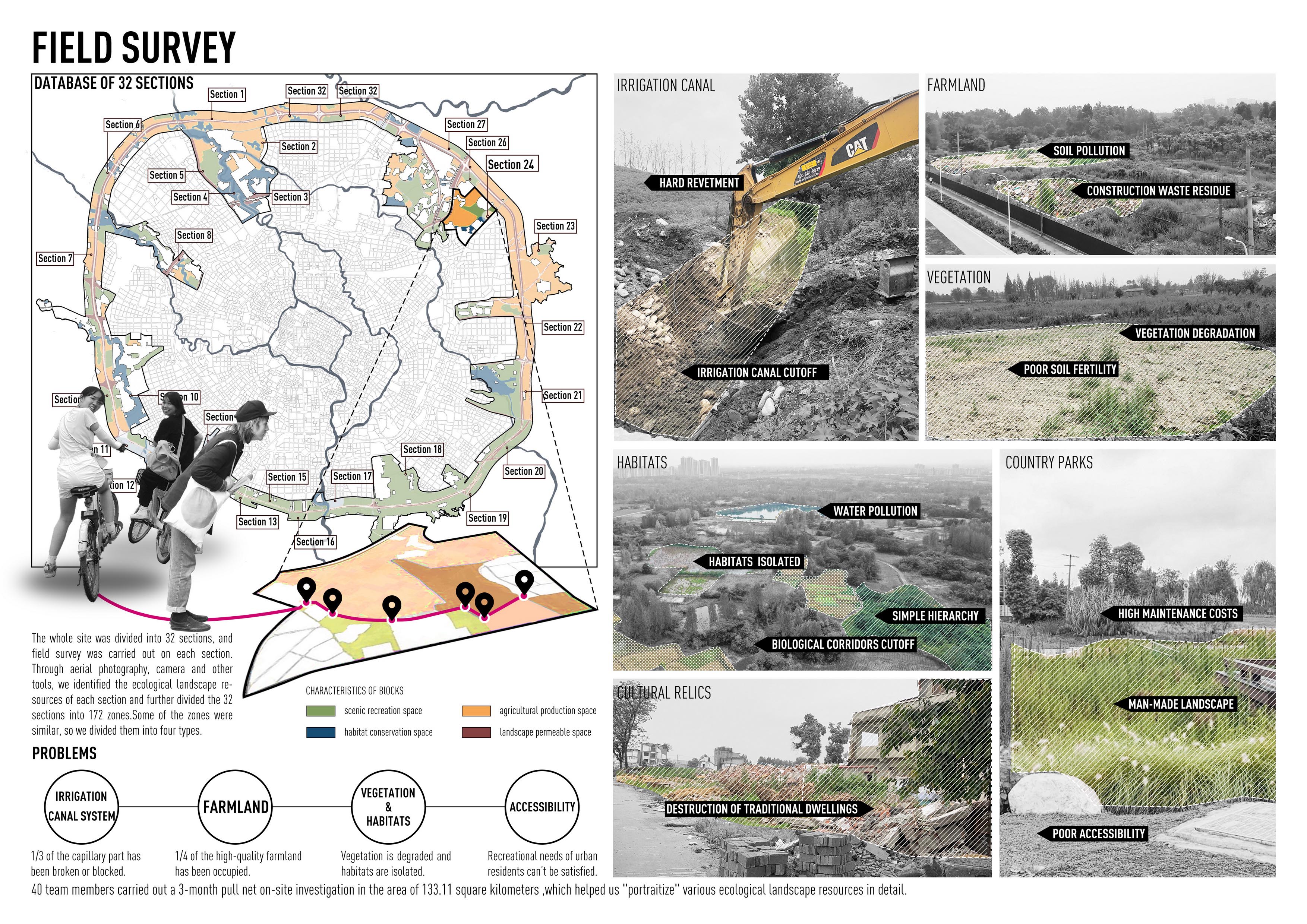
1)约1/3的传统灌渠体系废弛,水系尤其是毛细部分断裂严重,传统生态与人居格局缺少必要的自然要素支撑。
1)The traditional irrigation canal system is disappearing, about 1/3 of the capillary part has been broken or blocked, and the original ecosystem is increasingly fragmented.
2)近1/2优质农田已被侵占,成为周边工业和建筑垃圾堆放场,污染较为严重。
2) Nearly 1/4 of the high-quality farmland has been occupied, and become the surrounding industrial and construction waste dump, with serious pollution.
3)与农田、水渠共生的林草植被退化,层次趋向简单,较好生境相对孤立,生物栖息地、生境廊道等减少,动植物多样性严重下降。
3)The forest and grass vegetation symbiotic with farmland and canals is degraded, the hierarchy tends to be simple, habitats are relatively isolated, biological habitats and migration corridors are reduced, and the diversity of animals and plants is severely reduced..
4)部分保存尚好的绿色空间(郊野公园)和有价值的文化遗迹可达性弱,难以承载周边城市居民亟需的休闲游憩等功能需求。
4)The accessibility of some well-preserved green spaces (country parks) and cultural relics is weak, which is difficult to meet the recreational needs of surrounding urban residents.

调查与分析
Investigations and Analysis
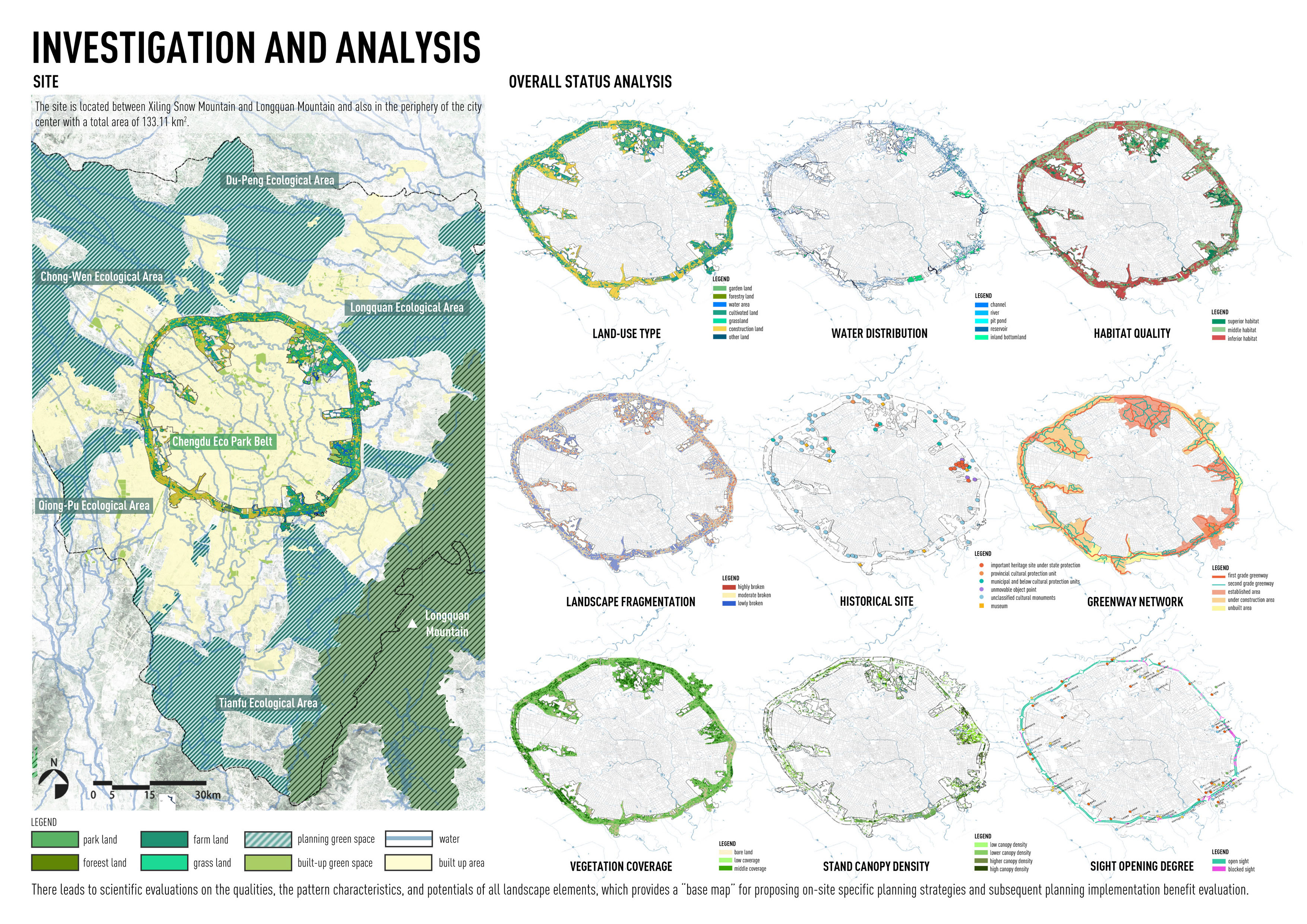
本项目建立了一个以风景园林专业引领,包括城乡规划、生态学、园林植物、信息技术等多领域合作的调查研究体系。
除对成都平原灌区历史和现状航空影像、植被和建设用地普查的数据进行宏观分析外,在133.11平方公里的范围内开展为期3个月的拉网式现场调查,第一次全面获取对其中各类生态景观资源进行详细的清点梳理和“画像”。在此基础上,构建起成都环城生态公园全域生态景观资源要素信息库,针对土壤及地表、农田、水网灌渠、植物群落、生境及栖息地、历史遗迹、绿道、眺望景观共八个层次的生态景观要素,对其资源水平、格局特征和提升潜力进行科学评估,为提出分类、分区景观提升规划策略和后续景观规划实施效益评估提供了良好的“基础底图”。
策略与实施

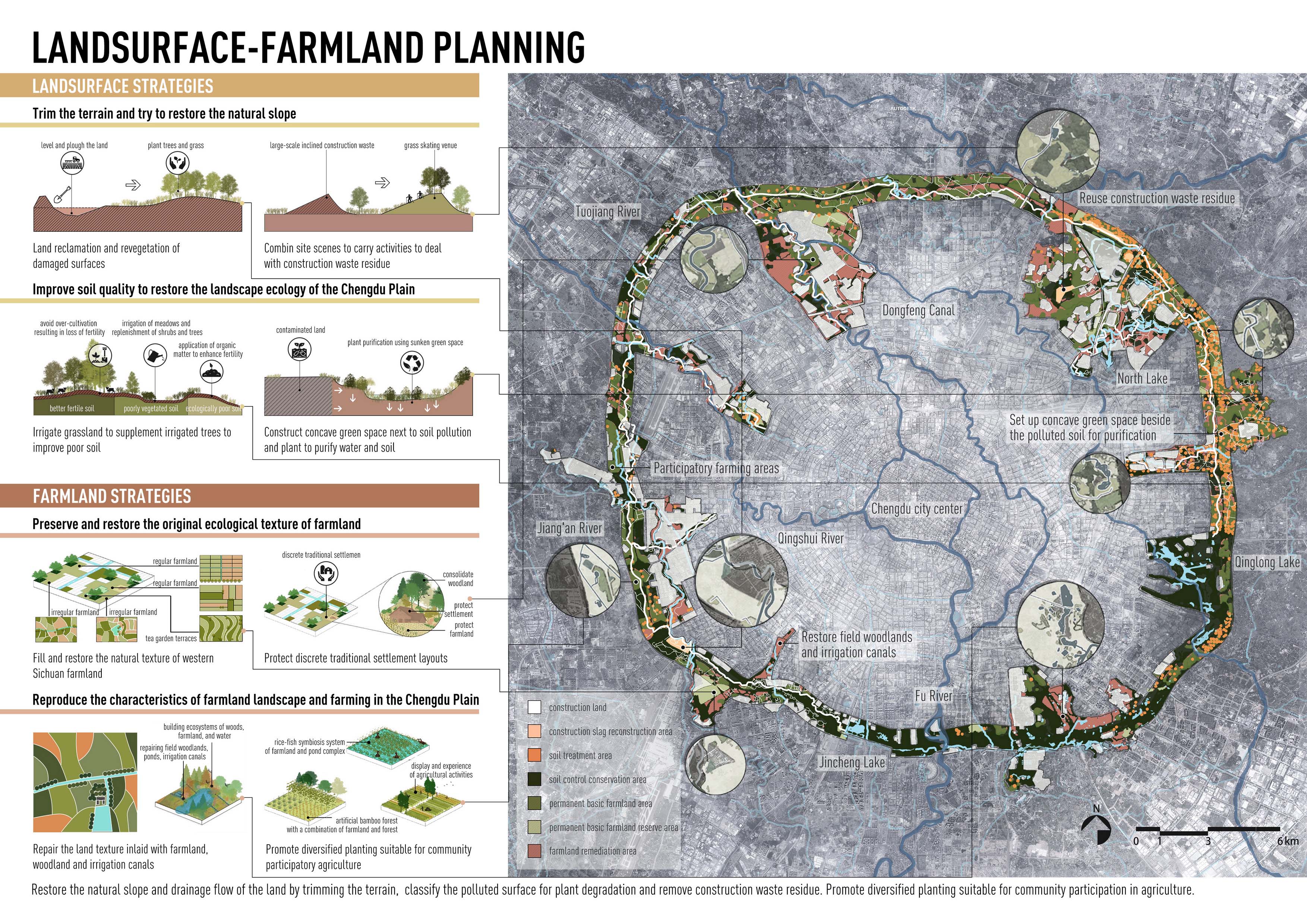
策略1,地表-农田规划:重塑地表肌理,和谐重组平原城市群与环城山水;处理裸露土壤并提升土质,恢复川西地景生态;建筑垃圾无害化处理与就地利用;处理土壤污染。以田为基,保留修复农田的原始生态肌理;以农为核,重现成都平原农田景观特色与农耕文化;优化农业种植及管理模式。
策略2,植物-生境规划:以林为屏,保护原生优质植物群落;凸显特色植物景观风貌,优化已建成植物群落;明确川西植物景观风格,控制新增植物群落结构;利用植物建植新技术,提高城市生物多样性。构建生态网络,营造完善的栖息地结构;分类型保护与修复栖息地;应用多种技术手段监测与修复栖息地。

策略3,水系-遗迹规划:保护贯通灌渠体系,构建“沟洫脉散”的全景水环境;保育和修复滨水生境,重塑稳定的自然过程;因势利导,净化灌区水系水体并提升水。保护修缮及利用居住遗址;引导建设景观建筑、构筑物;保护利用文化古迹。

策略4,绿道-眺望规划:利用现状良好的道路,强化绿道网络的地域性;尊重现状环境,赋予绿道不同的功能属性;引入绿色生态型技术,构建绿道基底的可持续性;协调绕城透绿景观,保护原有林地斑块。明确眺望对象,构建视觉廊道;优化眺望环境,提升眺望质量。

基于上述总体规划成果,充分吸收多领域专家、政府官员和公众意见,提出针对8大类生态景观要素层面的26项规划实施方法和80项技术指引,制作成都环城生态公园景观规划的“设计师手册”,为后续各项建设方案提供系统性指引;
搭建环城生态公园全域生态景观要素数字化信息平台,将133.11平方公里范围分为32个区段,172个片区,详细记录每个片区的生态景观基础信息及对应的“菜单式”技术导则,支撑全域动态监测与及时调控,优化维护绩效。

项目总结
Achievements and Summar
环城生态公园的规划建设为成都市2000多万市民、周边300万社区居民提供了最大的连续性绿色开放空间,塑造了“公园城市”理念下连接自然健康、优美场景和人民美好生活的纽带。其预期效益涵盖生态、社会等多个方面。
The planning and construction of Chengdu Eco-Park Belt provides the largest continuous green open space for more than 20 million citizens in Chengdu and 3 million residents in the surrounding neighborhoods, and creates well beings by linking communities with nature under the idea of "Park City”. It creates benefits in many aspects.
生态质量方面,一系列规划策略实现了大型绿色开放空间的精细化管理,更充分发挥绿色开放空间的生态效益。规划实施后重新连通灌渠约1750公里,恢复坑塘984.32公顷,新增下凹式绿地337.49公顷,承接汇水面积超过2233.53公顷。根据测算,规划实施后,环城生态公园将拥有成都平原90%的原生植物,增加昆虫、小型脊椎动物200余种,涵养水源量增加0.3亿立方米,每年增加固土量260万吨、固碳5.2万吨、释氧17万吨、滞尘12万吨。
In ecological aspect, the plan has realized the site-specific management of landscape resources and fully released the ecological benefits of green spaces. By the end of 2021, the area of brownfield in the Eco-Park Belt had been reduced by 1492.34 hectares, 1750 kilometers of irrigation canals had been reconnected, 984.32 hectares of pits and ponds had been restored, 337.49 hectares of concave green space had been added. There have re-owned 90% of native plants in Chengdu Plain, and more than 200 species of insects and small vertebrates have returned. It estimates that the annual increase of soil fixation is 2.6 million tons, carbon fixation is 52,000 tons, oxygen release is 170,000 tons and dust retention is 120,000 tons.
社会效益方面,到2021年底,建成绿道600公里、文化设施640处、体育设施1050处,与城市道路和周边社区相连接。 已成为市民休闲、自然教育、健身的首选之地,累计接待游客超过5000万人次。 COVID-19疫情发生以来,环城公园成功举办了“BFU国际造园节”、“天府绿道百公里接力赛”等多场大型公共活动,极大增强了成都绿环的活力与公众影响力。
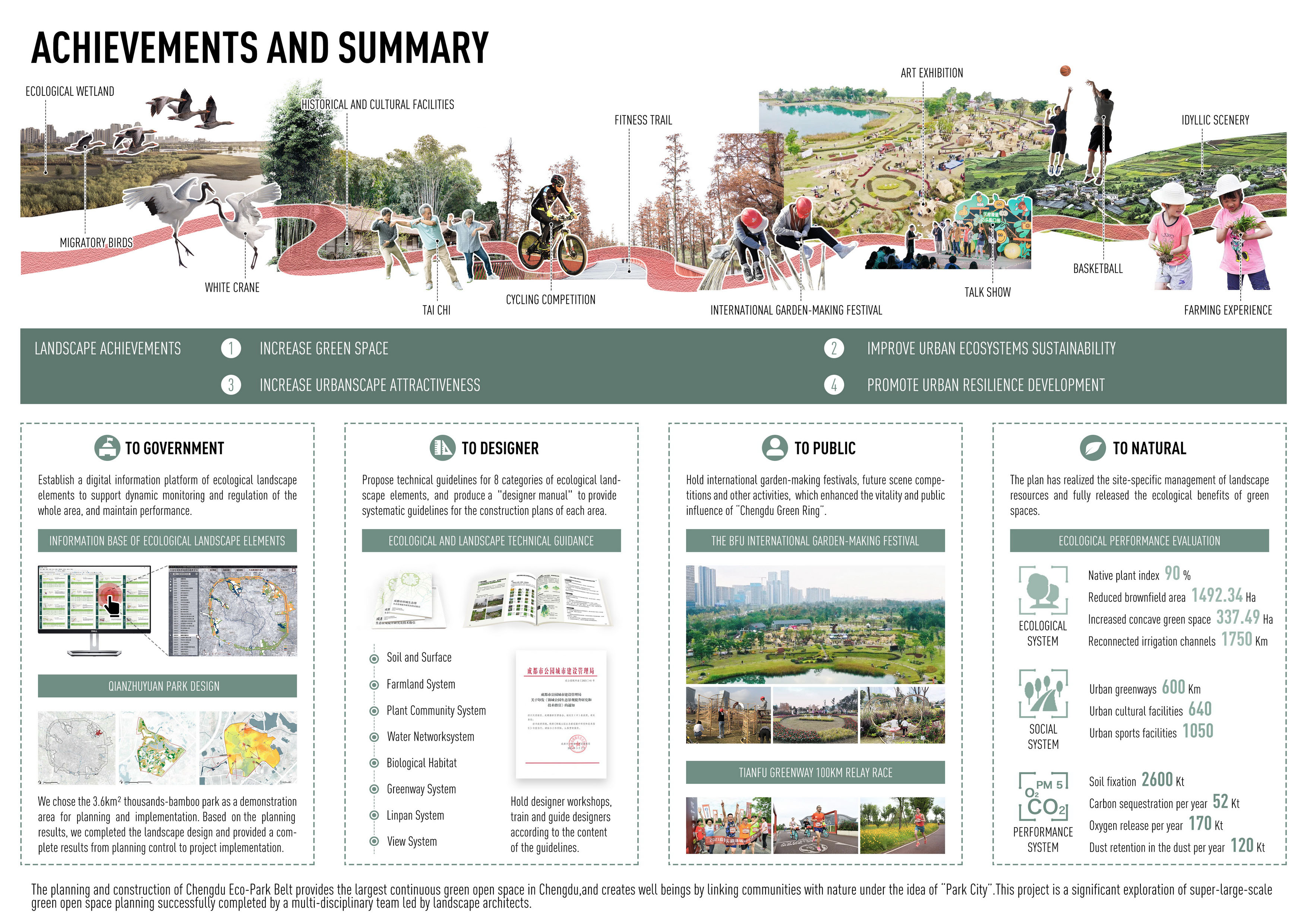
本项目是成功运用风景园林学引领的多学科技术体系完成的一次超大尺度绿色开放空间规划探索。一系列分析研究、规划措施期望为后工业时代的超大城市区域实现生态格局优化、景观质量提升、韧性网络构建等提供有价值的系统性解决方案。
This project is a significant exploration of super-large-scale green open space planning successfully completed by a multi- disciplinary team led by landscape architects. Aseries of investigation, analysis, and planning measures are expected to provide valuable systematic solutions for the optimization of ecological pattern, the improvement of landscape quality and the construction of resilient network in mega-city areas in the rapid urbanizing era.
主持设计师:王向荣,钱云,张晋石
设计团队:董丽,赵晶,魏方,王思元,徐昉,陈明坤,冯黎,周里云,黄楚梨,许少聪,钱蕾西,李见哲,雷春梅,刘怡凡,段雨汐,霍达,郑巧依,马文莉,吕方舟,李宏倩,王世琦,李辉,陈绮婷,赵崇豪,陈然,郭倩,李婷,陈馨,程瑜佳,李禾,张瑜,胡文玲,李玉婷,沈子晗,凌怡晨,郝慧超,邵壮,张烨
Leader designer:Wang Xiangrong, Qian Yun, Zhang Jin-shi
Design Team:Dong Li, Zhao Jing, Wei Fang, Wang Siyuan, Xu Fang, Chen Mingkun, Feng Li, Zhou Liyun, Huang Chuli, Xu Shaocong, Qian Leixi, Li Jianzhe, Lei Chunmei, Liu Yifan, Duan Yuxi, Huo Da, Zheng Qiaoyi , Ma Wenli, Lu Fangzhou, Li Hongqian, Wang Shiqi, Li Hui, Chen Qiting, Zhao Chonghao, Chen Ran, Guo Qian, Li Ting, Chen Xin, Cheng Yujia, Li He, Zhang Yu, Hu Wenling, Li Yuting, Shen Zihan, Ling Yichen, Hao Huichao, Shao Zhuang, Zhang Ye